The difference of the drinking habits in each region might cause the results. Besides, the relatively small number of studies included in the subgroup analyses might lead to the instability of the conclusions. When stratified by the end points, no significant association was 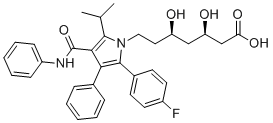 detected in either HGD or EAC or just EAC. It suggests that alcohol might be not associated in any stage of the Barrett’s esophagus progression. To our best knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis involving the relationship between alcohol consumption and risk of Butylhydroxyanisole development of Barrett’s esophagus. There are some strengths of this work. In the literature search, a large number of subjects were evaluated for the detection of the effect of the neoplastic risk in Barrett’s esophagus associated with alcohol drinking. Besides, through two independent methods, the publication bias wasn’t significant. The results of the sensitivity analysis suggest that the conclusions of this study were quite robust. These above results demonstrated that the conclusions of this meta-analysis were quite persuasive. Despite these advantages mentioned above, some limitations of the current meta-analysis should be acknowledged. First, the definitions of the case groups were not uniformly defined. Both the patients without higher alcohol intake or ever alcohol intake were obtained as the controls in the included studies. This would produce potential misclassification bias. While the subgroup analyses showed that no different results were detected and thus this might produce no serious problem. Secondly, even the categories of alcohol consumption are reported in some studies; however, the data were varied and broad. Thus, we were unable to determine the dose-response association between alcohol consumption and progression of Barrett’s esophagus. Third, it has been argued that because meta-analyses of observational studies may produce very precise, but spurious, results, a statistical combination of these data should not be the prominent component. However, considering that as an etiology exploring nature of this study, the pooled results of the observational studies would also provide certain improvement of the knowledge of the neoplastic development. The end, a combination of prognostic factors has been suggested to be required to define subgroups of patients at an increased risk of progression. However, the data of the included studies reported no sufficient data for an Folinic acid calcium salt pentahydrate Advanced research, which demonstrated the potential breakthrough. The forth, the understanding of the Barrett’s esophagus has developed in the recent years. The old conception says that although several different kinds of columnar epithelium can be found in the lower esophagus, it is only specialized intestinal metaplasia, distinguished by the presence of goblet cells, which increased the cancer risk. However, nowadays recent studies revealed that cardiac-type mucosa, columnar lined esophagus without goblet cells, also have the posibility of cancer development. With the development of understanding of Barrett’s esophagus, the older papers might provide results based on inaccurate definitions and thus the bias could not be ignored. Advanced well-designed studies based on both endoscopic results and histocytology are wanted in the future. In conclusion, on the basis of epidemiologic evidence, we found that alcohol consumption was not a neoplastic risk in Barrett’s esophagus. To get a more definitive conclusion, further pooled analyses with more complete raw data.
detected in either HGD or EAC or just EAC. It suggests that alcohol might be not associated in any stage of the Barrett’s esophagus progression. To our best knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis involving the relationship between alcohol consumption and risk of Butylhydroxyanisole development of Barrett’s esophagus. There are some strengths of this work. In the literature search, a large number of subjects were evaluated for the detection of the effect of the neoplastic risk in Barrett’s esophagus associated with alcohol drinking. Besides, through two independent methods, the publication bias wasn’t significant. The results of the sensitivity analysis suggest that the conclusions of this study were quite robust. These above results demonstrated that the conclusions of this meta-analysis were quite persuasive. Despite these advantages mentioned above, some limitations of the current meta-analysis should be acknowledged. First, the definitions of the case groups were not uniformly defined. Both the patients without higher alcohol intake or ever alcohol intake were obtained as the controls in the included studies. This would produce potential misclassification bias. While the subgroup analyses showed that no different results were detected and thus this might produce no serious problem. Secondly, even the categories of alcohol consumption are reported in some studies; however, the data were varied and broad. Thus, we were unable to determine the dose-response association between alcohol consumption and progression of Barrett’s esophagus. Third, it has been argued that because meta-analyses of observational studies may produce very precise, but spurious, results, a statistical combination of these data should not be the prominent component. However, considering that as an etiology exploring nature of this study, the pooled results of the observational studies would also provide certain improvement of the knowledge of the neoplastic development. The end, a combination of prognostic factors has been suggested to be required to define subgroups of patients at an increased risk of progression. However, the data of the included studies reported no sufficient data for an Folinic acid calcium salt pentahydrate Advanced research, which demonstrated the potential breakthrough. The forth, the understanding of the Barrett’s esophagus has developed in the recent years. The old conception says that although several different kinds of columnar epithelium can be found in the lower esophagus, it is only specialized intestinal metaplasia, distinguished by the presence of goblet cells, which increased the cancer risk. However, nowadays recent studies revealed that cardiac-type mucosa, columnar lined esophagus without goblet cells, also have the posibility of cancer development. With the development of understanding of Barrett’s esophagus, the older papers might provide results based on inaccurate definitions and thus the bias could not be ignored. Advanced well-designed studies based on both endoscopic results and histocytology are wanted in the future. In conclusion, on the basis of epidemiologic evidence, we found that alcohol consumption was not a neoplastic risk in Barrett’s esophagus. To get a more definitive conclusion, further pooled analyses with more complete raw data.
Month: May 2019
AITC can inhibit the growth of various types of tumor cells by causing cell cycle with antibody
This is why developing an assay, where multiple diabetes-associated autoantibodies would be measured simultaneously, is of very high interest. We propose that the same LFIA approach, as described in this article, could be adapted to the simultaneous detection of other islet autoantibodies on the same test strip. For this capture antibodies with very high affinity are needed. In conclusion, we have developed a novel LFIA based on a bridging format which enables rapid and practical detection of IA2As in human serum samples. Its key advantages are its simplicity and its fast readout, which means that our IA-2A LFIA could easily be used for preliminary screening of at-risk individuals and for diagnostic assessment of T1D directly in an outpatient hospital setting. Inflammatory bowel disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder, of which there are two major types��Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Povidone iodine Although the etiopathogenesis of IBD has not been definitively elucidated, it is widely accepted that both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis result from a complex interaction between genetic, environmental, and intestinal immune factors. IBD is also known to be associated with extensive edema-induced tissue injury and remodeling, inflammatory cell infiltration, numerical or functional alteration of immune cell subpopulations, loss of epithelial integrity, and increased angiogenesis. These features 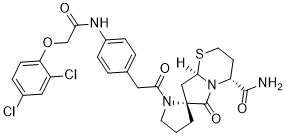 are thought to contribute to the pathophysiology and development of IBD through diverse molecular mechanisms that can involve several cell types and mediators. Angiogenesis is now known to be intimately involved in a number of biological processes, including growth, development, and tissue repair. In some disease states such as tumorigenesis and chronic inflammation, angiogenesis becomes pathologic and therefore represents a potential therapeutic target. There is Miglitol considerable evidence that abnormal angiogenesis is a key pathology of many chronic inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, and diabetic retinopathy. Recent human and animal studies revealed that angiogenesis also plays a crucial role in IBD. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A is an important angiogenic mitogen that has become the primary target for antiangiogenic drug therapies. VEGF-A is a fundamental mediator of pathologic angiogenesis in several inflammatory disorders, including neoplasia, chronic inflammation, and IBD. The microvasculature in IBD likely contributes to bowel inflammation by affecting innate immunity, leukocyte infiltration, coagulation, and vascular permeability. A number of studies have demonstrated that direct inhibition of VEGF or its primary receptor VEGFR2 decreases inflammation and can potentially lessen colonic tissue damage by reducing vascularization or by altering vessel permeability. In human and experimentally modeled IBD, the reduced vascularization induced by VEGF decreases the delivery of inflammatory cells to colonic injury sites, thereby disrupting the damaging inflammation-angiogenesis cycle. One class of compounds that may be useful for treating IBD is the isothiocyanates, which are found as thioglucoside conjugates known as glucosinolates in many cruciferous vegetables like cabbage, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts. Many ITCs can prevent the development of chemically induced tumors in a variety of animals. Allyl isothiocyanate is a cancer chemopreventive phytochemical agent found in many dietary sources.
are thought to contribute to the pathophysiology and development of IBD through diverse molecular mechanisms that can involve several cell types and mediators. Angiogenesis is now known to be intimately involved in a number of biological processes, including growth, development, and tissue repair. In some disease states such as tumorigenesis and chronic inflammation, angiogenesis becomes pathologic and therefore represents a potential therapeutic target. There is Miglitol considerable evidence that abnormal angiogenesis is a key pathology of many chronic inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, and diabetic retinopathy. Recent human and animal studies revealed that angiogenesis also plays a crucial role in IBD. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A is an important angiogenic mitogen that has become the primary target for antiangiogenic drug therapies. VEGF-A is a fundamental mediator of pathologic angiogenesis in several inflammatory disorders, including neoplasia, chronic inflammation, and IBD. The microvasculature in IBD likely contributes to bowel inflammation by affecting innate immunity, leukocyte infiltration, coagulation, and vascular permeability. A number of studies have demonstrated that direct inhibition of VEGF or its primary receptor VEGFR2 decreases inflammation and can potentially lessen colonic tissue damage by reducing vascularization or by altering vessel permeability. In human and experimentally modeled IBD, the reduced vascularization induced by VEGF decreases the delivery of inflammatory cells to colonic injury sites, thereby disrupting the damaging inflammation-angiogenesis cycle. One class of compounds that may be useful for treating IBD is the isothiocyanates, which are found as thioglucoside conjugates known as glucosinolates in many cruciferous vegetables like cabbage, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts. Many ITCs can prevent the development of chemically induced tumors in a variety of animals. Allyl isothiocyanate is a cancer chemopreventive phytochemical agent found in many dietary sources.
The experiments with products of asymmetric PCRs indicated that the cause of the described phenomena
Single stranded DNA is an often unattended by-product of a PCR and also an ingredient of every hybridization approach which contains PCR-products. Total ssDNA comprises of abortion products, which are generated when the polymerase dissociates from its template during Diperodon elongation, and full-length products. Single stranded full-length products may exist only of one type of strand at a time because two complementary strands would hybridize with each other. Therefore, only the excess strand is available as ssDNA and can hybridize directly to its corresponding probe. We developed a new model for the hybridization mechanism which relies on the principle that dsDNA is almost unable to bind to capture probes without ssDNA as catalyst. A possible mechanism of ssDNA induced probe hybridization would be that at first the excess strand hybridizes to its probe. The resulting dangling ends could again act as probes as described earlier. These single stranded dangling ends would have two advantages in binding to double stranded PCR-products compared to covalently bound oligonucleotide probes. On the one hand, they are generally much longer, resulting in a more stable hybridization. On the other hand, their terminal sequence matches the sequence of the end of the PCR-product. Denaturing of a few bases is much more likely to occur at the end of a double stranded PCR-product than in the middle of it. This could enable the dangling tail to attack this end and partially hybridize to its complementary strand. Via a branch migration mechanism the former dangling end could displace the other strand. A complete release of this strand 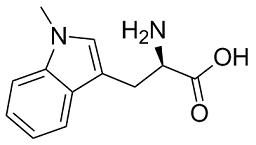 would regenerate the original free ssDNA enabling further reaction cycles. According to the mentioned mechanisms, the displacement of probe bound dsDNA is also possible, so that dissolved and attached dsDNA are in steady state equilibrium after some time. The proposed mechanism shown in Figure 9 is theoretically, and several similar reaction mechanisms are imaginable, such as a further branching of the strand agglomerate shown in Figure 9 C forming branched DNA, as observed recently. Aggregates of multiple sense and antisense strands bound to capture probes have been described already. A beneficial effect of increased ssDNA generation on microarray signals, for example by asymmetric PCR, has already been described, too, but the mechanism of action has not been characterized, yet. Another method already in use to increase the ssDNA content in the hybridization mixture is to initially separate the strands of the PCR-product by heat denaturation. However, the amount of ssDNA declines over time due to renaturation of both strands. Our experiments indicate that ssDNA strongly enhances the hybridization of PCR-products to the probe configuration specific for the ssDNA. The increased generation of one specific strand in an asymmetric PCR and the addition of synthetic ssDNA, respectively, had led to drastic changes of the s/as-ratio of some probes. According to our model, the addition of synthetic sense ssDNA increased the signal of antisense probes by providing a catalyst for the hybridization and decreased the signal of the sense probe in return by reducing the amount of free antisense strand. The considerable extent of the signal shift supports the assumption that ssDNA is essential for efficient hybridization. In an equimolar PCR, a signal shift of some probes could be observed, too, when the overall primer Amikacin hydrate concentration in the PCR was reduced.
would regenerate the original free ssDNA enabling further reaction cycles. According to the mentioned mechanisms, the displacement of probe bound dsDNA is also possible, so that dissolved and attached dsDNA are in steady state equilibrium after some time. The proposed mechanism shown in Figure 9 is theoretically, and several similar reaction mechanisms are imaginable, such as a further branching of the strand agglomerate shown in Figure 9 C forming branched DNA, as observed recently. Aggregates of multiple sense and antisense strands bound to capture probes have been described already. A beneficial effect of increased ssDNA generation on microarray signals, for example by asymmetric PCR, has already been described, too, but the mechanism of action has not been characterized, yet. Another method already in use to increase the ssDNA content in the hybridization mixture is to initially separate the strands of the PCR-product by heat denaturation. However, the amount of ssDNA declines over time due to renaturation of both strands. Our experiments indicate that ssDNA strongly enhances the hybridization of PCR-products to the probe configuration specific for the ssDNA. The increased generation of one specific strand in an asymmetric PCR and the addition of synthetic ssDNA, respectively, had led to drastic changes of the s/as-ratio of some probes. According to our model, the addition of synthetic sense ssDNA increased the signal of antisense probes by providing a catalyst for the hybridization and decreased the signal of the sense probe in return by reducing the amount of free antisense strand. The considerable extent of the signal shift supports the assumption that ssDNA is essential for efficient hybridization. In an equimolar PCR, a signal shift of some probes could be observed, too, when the overall primer Amikacin hydrate concentration in the PCR was reduced.